In this tutorial, you will learn how to create an application that uses Google Maps API to determine the precise location of another user. We will achieve this by saving the users location on the Firebase Realtime Database and then retrieving the data from another device.
Location services have recently become common among social apps that we use from day to day. Furthermore, these services can be used to track a lost or stolen device. Therefore, knowing how to implement location services can allow you to create more productive applications.
Goal
From this tutorial, you will be able to come up with two simple applications to aid with location tracking. These projects use the Google Maps API and Firebase’s Realtime Database.
Pre-requisites
- A good understanding of Kotlin in Android development.
- Android Studio.
For this tutorial, we shall use real Android devices for testing. However, you can use an emulator by mocking location data. You can read more here
Step 1 – Create a new project
Create a new project on Android Studio. On the select Project template page, choose the Google Maps Activity template.
![]()
Wait for Android Studio to build your project.
At this point after running the app you will see a blank screen, because you are yet to set up the API key for the map.
A few things to note
Once you open the AndroidManifest.xml, you will see these auto-filled details:
ACCESS_FINE_LOCATIONpermission. This accesses the user’s precise location. Mostly used when you require the most accurate location. Another type of location accuracy is theACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION, which is less accurate. Therefore, we shall be working with theACCESS_FINE_LOCATIONfor accurate readings.- The
com.google.android.geo.API_KEYspecifies the API key.
implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:17.0.0'
Step 2 – Create an API key
You need to create an API key and enable it in the developer console before working with the Google Maps API. Use your Google account to sign up for this.
Open res/values/google_maps_api.xml. This is what you will see.
![]()
This file will contain your API key. Click on the underlined link and press create a project and continue.
![]()
In the next screen, you will need to create an API key to call the API.
![]()
The API key is in purple.
![]()
Once you have the API key, copy and paste it in the value of google_maps_key in the XML file.
The MapsActivity
This is an overview of the default MapsActivity.
class MapsActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback {
private lateinit var mMap: GoogleMap
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps)
val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager
.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this)
}
// This method is called when we need to initialize the map and as you can see, it creates a marker with coordinates near Sydney and adds it to the map.
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) {
mMap = googleMap
// Add a marker in Sydney and move the camera
val sydney = LatLng(-34.0, 151.0)
mMap.addMarker(MarkerOptions().position(sydney).title("Marker in Sydney"))
//call moveCamera() on mMap to update the camera
mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(sydney))
}
}
At this point, once you run the app, you will notice that the marker is in Sydney.
Step 3 – Creating a Firebase project
We will use Firebase to store the user’s location. Once again, you will need a Google account. You can sign up here.
![]()
Step 4 – Connect the Firebase project to the app
You now need to connect the project to your app.
- Go to tools>firebase
![]()
Make sure you add the Realtime Database to your app.
Step 5 – Add permissions
- Add the internet permission.
This permission allows the application to connect to the internet and save data.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
- Add the Google Maps location dependency.
implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-location:17.0.0'
Step 6 – The MapsActivity
Navigate to MapsActivity.kt and add the following code.
class MapsActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback {
private lateinit var map: GoogleMap
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps)
// Obtain the SupportMapFragment and get notified when the map is ready to be used.
val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager
.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this)
setupLocClient()
}
private lateinit var fusedLocClient: FusedLocationProviderClient
// use it to request location updates and get the latest location
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) {
map = googleMap //initialise map
getCurrentLocation()
}
private fun setupLocClient() {
fusedLocClient =
LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this)
}
// prompt the user to grant/deny access
private fun requestLocPermissions() {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this,
arrayOf(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION), //permission in the manifest
REQUEST_LOCATION)
}
companion object {
private const val REQUEST_LOCATION = 1 //request code to identify specific permission request
private const val TAG = "MapsActivity" // for debugging
}
private fun getCurrentLocation() {
// Check if the ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission was granted before requesting a location
if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) !=
PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
// call requestLocPermissions() if permission isn't granted
requestLocPermissions()
} else {
fusedLocClient.lastLocation.addOnCompleteListener {
// lastLocation is a task running in the background
val location = it.result //obtain location
//reference to the database
val database: FirebaseDatabase = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance()
val ref: DatabaseReference = database.getReference("test")
if (location != null) {
val latLng = LatLng(location.latitude, location.longitude)
// create a marker at the exact location
map.addMarker(MarkerOptions().position(latLng)
.title("You are currently here!"))
// create an object that will specify how the camera will be updated
val update = CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(latLng, 16.0f)
map.moveCamera(update)
//Save the location data to the database
ref.setValue(location)
} else {
// if location is null , log an error message
Log.e(TAG, "No location found")
}
}
}
}
override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(
requestCode: Int,
permissions: Array<String>,
grantResults: IntArray) {
//check if the request code matches the REQUEST_LOCATION
if (requestCode == REQUEST_LOCATION)
{
//check if grantResults contains PERMISSION_GRANTED.If it does, call getCurrentLocation()
if (grantResults.size == 1 && grantResults[0] ==
PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
getCurrentLocation()
} else {
//if it doesn`t log an error message
Log.e(TAG, "Location permission has been denied")
}
}
}
}
Step 7 – Run the app
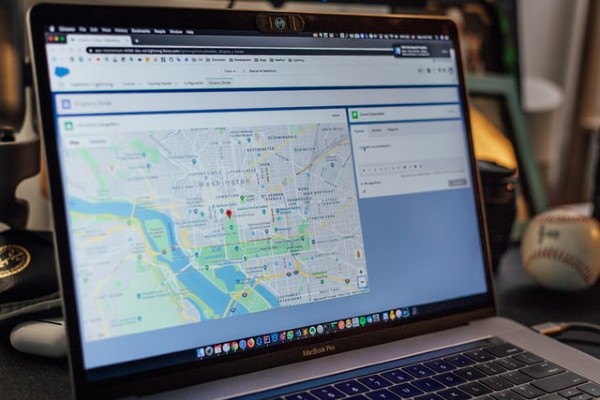
Run the app. This is what you will achieve (locations may differ). Give the app location permission.
![]()
The user location will be seen as shown below:
![]()
From the code above, you have successfully saved the user’s location in a database. Navigate to the Firebase console and click on the project you had created.
You should see something similar to this.
![]()
The LocationChecker app
This second application allows you to retrieve the user’s location from the database.
Step 1: Creating a new project
Follow the process discussed above to create a new project. Make sure you select the Google Maps template and name it appropriately.
Step 2: Add credentials to an existing key
Since we already have an API key, we can just include it in the console. Open your developer’s console and click on the edit icon.
![]()
Navigate to the google_maps_api.xml file and copy the package name and SHA-1 certificate fingerprint, paste these details on the add item section. Then, save the changes.
Step 3: Adding a button
We need to add a button that will trigger the reading of the current location in the database.
Here is the activity_maps.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
xmlns:map="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MapsActivity"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/map"
android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
map:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
map:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
map:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
map:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
map:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
map:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
map:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
android:padding="20dp"
android:id="@+id/btn_find_location"
android:text="@string/find_user_s_location"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Step 4: Adding permissions
By default, the GoogleMaps activity template adds the ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission in the AndroidManifest.xml file. Since we need the internet to read from the database, add the internet permission, as shown below:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
Step 4: The model class
Since we are reading from the database, we need a class that will add the attributes, latitude, and longitude to handle data.
import com.google.firebase.database.IgnoreExtraProperties
@IgnoreExtraProperties
data class LocationInfo(
var latitude: Double? = 0.0,
var longitude: Double? = 0.0
)
Step 5: The MapsActivity
Add the following code:
class MapsActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OnMapReadyCallback {
private lateinit var map: GoogleMap
private var database: FirebaseDatabase = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance()
private var dbReference: DatabaseReference = database.getReference("test")
private lateinit var find_location_btn: Button
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_maps)
find_location_btn = findViewById(R.id.btn_find_location)
// Obtain the SupportMapFragment and get notified when the map is ready to be used.
val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager
.findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this)
// Get a reference from the database so that the app can read and write operations
dbReference = Firebase.database.reference
dbReference.addValueEventListener(locListener)
}
val locListener = object : ValueEventListener {
// @SuppressLint("LongLogTag")
override fun onDataChange(snapshot: DataSnapshot) {
if(snapshot.exists()){
//get the exact longitude and latitude from the database "test"
val location = snapshot.child("test").getValue(LocationInfo::class.java)
val locationLat = location?.latitude
val locationLong = location?.longitude
//trigger reading of location from database using the button
find_location_btn.setOnClickListener {
// check if the latitude and longitude is not null
if (locationLat != null && locationLong!= null) {
// create a LatLng object from location
val latLng = LatLng(locationLat, locationLong)
//create a marker at the read location and display it on the map
map.addMarker(MarkerOptions().position(latLng)
.title("The user is currently here"))
//specify how the map camera is updated
val update = CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(latLng, 16.0f)
//update the camera with the CameraUpdate object
map.moveCamera(update)
}
else {
// if location is null , log an error message
Log.e(TAG, "user location cannot be found")
}
}
}
}
// show this toast if there is an error while reading from the database
override fun onCancelled(error: DatabaseError) {
Toast.makeText(applicationContext, "Could not read from database", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
}
}
override fun onMapReady(googleMap: GoogleMap) {
map = googleMap //initialize map when the map is ready
}
companion object {
// TAG is passed into the Log.e methods used above to print information to the Logcat window
private const val TAG = "MapsActivity" // for debugging
}
}
When you run the app, you should be able to get a similar view (locations will differ):
![]()
Testing the apps
Install both apps on your phone. Make sure the internet connection is good. Check the database for the saved location. On the second app, LocationChecker, check if the location was retrieved.
You can download these projects from here and here.
Conclusion
You can use the Maps API to create awesome apps or add more functionalities to existing ones. You can also add other features that might interest you. For instance, you can notify the user that they are being tracked.
Happy coding!!








Comments: